Technological innovations over the past decades that have seen a recent acceleration have been the driving force behind a new digital revolution in healthcare. Thanks to this research, there is the prospect of optimising the functioning of treatments and vaccines and facilitating the work of physicians. Research on the possibility of using artificial intelligence in healthcare is based on several needs, including data regarding ageing. In addition to an increase in life expectancy, the future of healthcare will soon have to deal with the shortage of medical personnel (after all, the long-standing issue regarding primary care physicians is well known).
Fortunately, the tools available to the entire healthcare system are increasingly innovative thanks to the digital revolution in healthcare. These changes lead, in turn, to a development in communications between patients, physicians, pharmacists, and pharmaceutical companies. The very concept of “wellness” is undergoing a mutation considering recent digital innovations. Experts often debate the digital transformation’s impact on the healthcare system in this area.
The future of healthcare is artificial intelligence
The healthcare sector is undergoing a revolution, supported by the many prolific research studies on the application of artificial intelligence in healthcare. These studies cover a variety of fields, from prevention and diagnostics to the organisation of the healthcare system and drug and vaccine development. In the recent emergency, artificial intelligence has enabled physicians to make informed clinical decisions and better manage emergencies. For example, AlphaFold is an artificial intelligence program that can build the 3-D structure of a protein and its amino acid sequence. Such a system is essential because analysing the protein’s design makes it possible to determine how it functions. According to recent research, the United States spends about $7.6 trillion on health care; of this enormous figure, waste accounts for about 30 to 40 per cent.

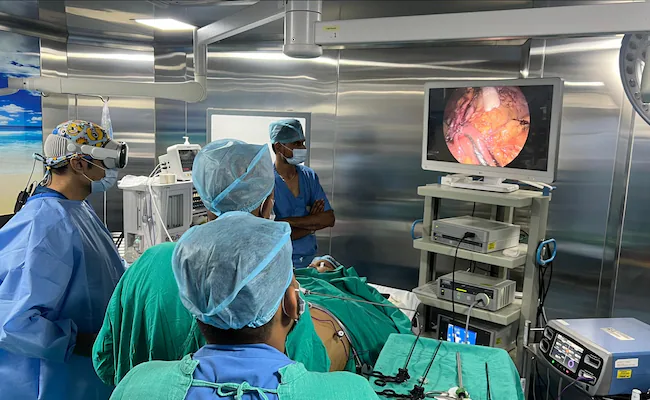
New technologies bring meaningful innovations to the medical sector as well, not only regarding the management of big data but also regarding the possibility of benefiting from artificial intelligence and augmented reality in this area as well. The extension of the average lifespan owes much to the countless scientific and technological breakthroughs which have enabled the adoption of innovative and increasingly reliable tools within operating rooms.
When we hear about technological innovation, we immediately think it is only about the devices we use daily: tablets, computers, iPhones. However, innovation consists precisely in bringing technology into areas not traditionally connected to the digital world. Research has made many advances in electronics, robotics, and technology, intending to create devices that can help medicine. Just think of the da Vinci Robot, organs or limbs made with 3D printers, robotic neurorehabilitation, or sophisticated artificial limbs through which even tactile function can be recovered.
Digital revolution in Google, Microsoft and Amazon in the healthcare sector
In 2016, Google and French pharmaceutical giant Sanofi announced a $500 million investment in a joint venture to develop treatments for people with diabetes. It involves special contact lenses equipped with sensors to detect blood sugar levels. Amazon is also entering the artificial intelligence (AI) industry. In fact, Alexa, Amazon’s voice recognition system, is being experimented with in the United States to aid surgeons in operating rooms. Regarding augmented reality, on the other hand, HoloLens, Microsoft’s visors, considered a viable and incredibly inexpensive alternative to traditional medical equipment, are entering U.S. operating rooms. Orthopaedic surgeons are testing these glasses in the Brazilian city of Santa Caterina to perform spine surgery. With the wearable, spinal surgeons can view a series of 3-D projections of the targeted area and determine the best way to attach screws to the spine.
A survey conducted by the European Commission shows that 59 per cent of respondents use the Internet to research health issues, and more and more citizens say they use digital channels to communicate with their primary care physician. New digital technologies have revolutionized the doctor-patient relationship. Each person can access data on their health status in real-time, share fears and expectations with other patients, and compare notes on possible side effects of medications. All this is thanks to the tools made available by e-Health and m-Health.