Cyberattack increased defined
According to Check Point Research (CPR), worldwide cyberattacks increased by 28% in the 3rd quarter of 2022 compared to the same period of the previous year.
In 2022, cybercriminals and state-linked actors continued to exploit the hybrid working practices of organizations, and the growth of these attacks does not appear to be slowing down as the Russia-Ukraine conflict continues to have a profound impact globally. Organizations need to consolidate and automate their security infrastructure to monitor better and manage attack surfaces and prevent threats with less complexity and less need for staff.
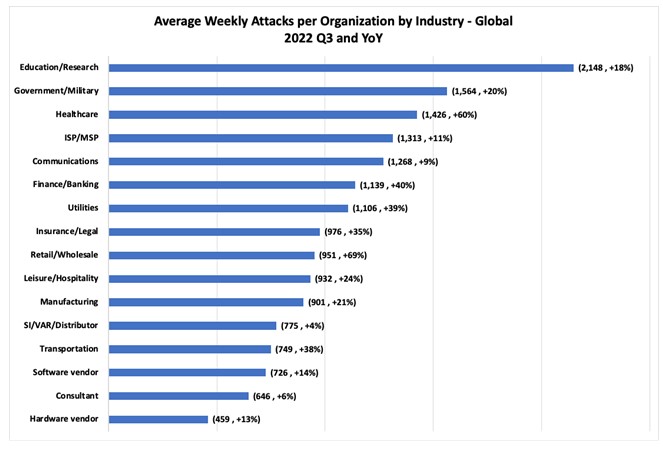
Asia experienced the highest cyberattack volume, with 1,778 weekly attacks per organization. The industry most attacked in Q3 of the year for total cyberattacks was Education/Research, with an average of 2,148 attacks per organization weekly, an 18% increase compared to Q3 2021.
Cybercriminals and state-linked actors have continued to exploit the hybrid working practices of organizations, and the growth of these attacks does not appear to be slowing down as the Russia-Ukraine conflict continues to have a profound impact globally. Organizations expect to consolidate and automate their security infrastructure to monitor better and manage attack surfaces and prevent threats with less complexity and less need for staff.
Great Phenomena of cyberattacks increased
According to Check Point Research (CPR) data, the healthcare industry was the most targeted by ransomware in the third quarter of 2022, with one in 42 organizations affected by ransomware, an increase of 5% year-over-year. This was followed by the Internet Services/Managed Service Providers sector (1 in 43 organizations affected, down 25% year-over-year), the Financial Services/Banking industry (1 in 49 organizations affected by ransomware, up 17% from last year), and Retail/Wholesale, which saw the most significant year-over-year increase in ransomware attacks, up 4.39% from Q3 2021.
We enter the festive season, so hacker attacks increase during off hours when security is considered less intense. Ransomware cybercriminal groups have focused their attention on hospitals because of the intense pressure on them to cover similar cases. CPR is warning healthcare organizations to remain vigilant as the end of the year approaches.
Asia experienced the highest cyberattack volume, with 1,778 weekly attacks per organization.
Features and Characteristics for mitigation CyberAttacks increased
New national cybercrime taskforces: more governments to follow Singapore’s lead in creating agency taskforces to tackle ransomware and cybercrime, bringing together businesses, government departments, and law enforcement to combat the growing threat to trade and consumers. These efforts are partly the result of questions about whether the cyber insurance sector can be considered a safety net for cyber incidents.
For example, the breach at Australian telco Optus led the country’s government to introduce new data breach regulations that other telcos must follow to protect customers from subsequent fraud. We will see other national governments follow suit in 2023 in addition to existing measures such as GDPR.
The global cyber skills gap will increase by more than 25% in 2022. It is noteworthy that the automotive industry has already moved to establish measures to protect the data of vehicle owners. Other consumer goods sectors will follow this example that store and processes data, making manufacturers responsible for product vulnerabilities. However, due to the pandemic, organizations and multinationals have more complex, distributed networks and cloud deployments than ever. Security teams must consolidate their IT and security infrastructure to improve their defences and reduce their workload to help them stay ahead of threats.
Future use or projections
According to Oded Vanunu (Head of Products Vulnerability Research, Check Point Software): «There is a dramatic increase in digital fraud due to the global economic slowdown and inflation. Cybercriminals will increasingly turn to social media campaigns via telegram, WhatsApp, and other popular messaging apps. There will also be more cyberattacks on Web3 blockchain platforms, mainly to take over the platforms and their users’ crypto assets.”
Another exciting view and prediction are from Deryck Mitchelson (EMEA CISO, Check Point): “Cloud transformation will be slowed by cost and complexity, with many companies considering moving operations back in-house or to private data centers to reduce their overall threat surface.”



