The startup behind the Chinese artificial intelligence (AI) application DeepSeek, which made waves in the market with the launch of its latest model, has completed a full week of open-source code releases. The company made five code repositories public, aiming to demonstrate its public commitment to “total transparency.” “As part of the open-source community, we believe that every shared line of code adds to the collective momentum, accelerating progress. Daily unlocks are coming. No ivory towers, just pure garage energy and community-driven innovation,” the company stated ahead of the release.
DeepSeek’s dedication to open-source sets it apart from most Chinese AI companies, which, like their American counterparts, with notable exceptions such as Meta’s Llama models or X’s Grok, tend to favour closed-source models. The company’s founder, Liang Wenfeng, stated in a July interview that DeepSeek does not prioritise the commercialisation of its AI models and believes open-source carries soft power. “When others build upon your innovation, it brings a great sense of accomplishment,” Liang said. “In fact, open-source is more of a cultural practice than a commercial one, and contributing to it earns us respect,” he continued.
Revealing the ingredients of the secret sauce
The newly released open-source code provides the supporting infrastructure for the AI models that DeepSeek has already shared publicly, building upon existing open-source frameworks.

On Day 6 of what they named “#OpenSourceWeek,” the company unveiled an overview of its DeepSeek-V3/R1 inference system, showcasing efficiency improvements, including cross-node EP-powered batch scaling, computation-communication overlap, and expert-parallel load balancing. These advancements aim to maximize throughput while reducing latency, reinforcing what DeepSeek calls its pursuit of “high-performance AI.”
DeepSeek open-source
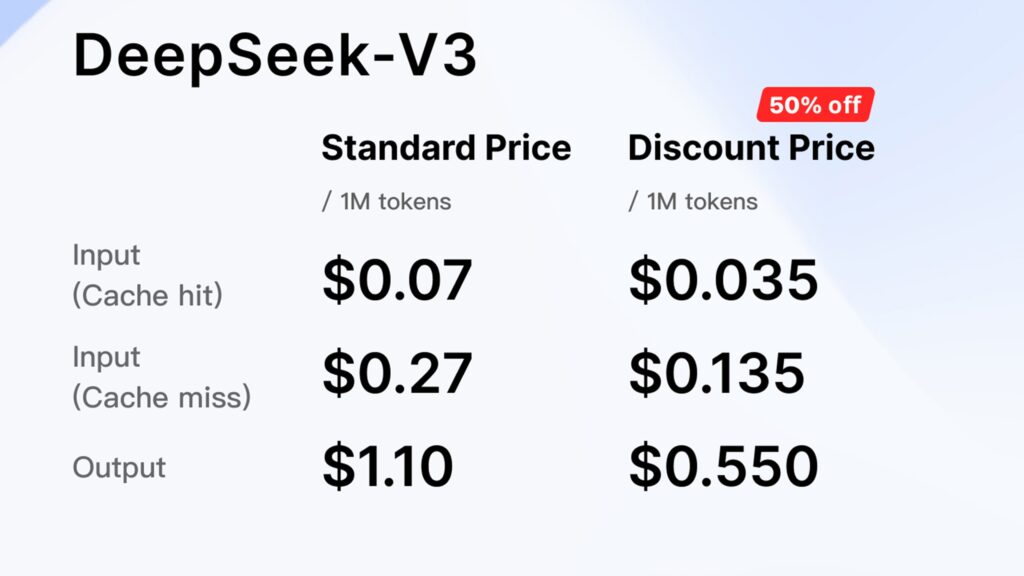
Earlier in the week, DeepSeek introduced key infrastructure upgrades, such as the Fire-Flyer File System (3FS), a parallel file system that enables an aggregate read throughput of 6.6 TiB/s in a 180-node cluster. The company also shared two innovative parallelism strategies: DualPipe, a bidirectional pipeline parallelism algorithm, and EPLB, an expert-parallel load balancer designed to enhance training efficiency. In a move to encourage broader adoption, DeepSeek also announced steep off-peak discounts on its API platform, slashing prices by up to 75%.
DeepSeek leads the Chinese AI race, but questions remain
The data release followed DeepSeek’s launch of a new algorithm called Native Sparse Attention (NSA), designed to improve training and inference efficiency in long-context scenarios. DeepSeek’s rapid rise has been reflected in its growing user base. Since its launch in 2023 by the Chinese hedge fund High-Flyer Quant, the platform has surged in popularity. As of January, it was China’s most-used chatbot service, boasting 22.2 million daily active users, surpassing Douban’s 16.95 million, according to the South China Morning Post.
However, DeepSeek’s rapid ascent has also sparked questions about the origins of its training data. Although the business bills itself as an open-source model and makes some of its outputs available to the public, the complete transparency of the training data and code that underlie it is still unknown.



