Open Ran define
The open radio network is essentially an agreement of standards and protocols between all the vendors that make this hardware interoperable and tolerant of implementing 5G and later 6G network technology.
Major European providers are committed to developing the Open Radio Access Network (Open RAN). The cooperation aims to ensure a framework for creating an interoperable market for open wireless access networks and the availability of solutions for their timely deployment in Europe. An open, ‘smart’, virtual, and fully interoperable Radio Network (enabling more effective and efficient mobile communications) is essential if Europe is to provide 5G to all by 2030. It will help create stronger and more resilient supply chains and platforms and promote digital autonomy and uninterrupted technology leadership.
Due to new open architectures, software, and hardware, such as Open RAN, operators can extend 5G to more users in a cost-effective, secure, and energy-efficient way. This flexibility will encourage even more innovation across industries and in areas such as telemedicine and intelligent factories.
Technical Part
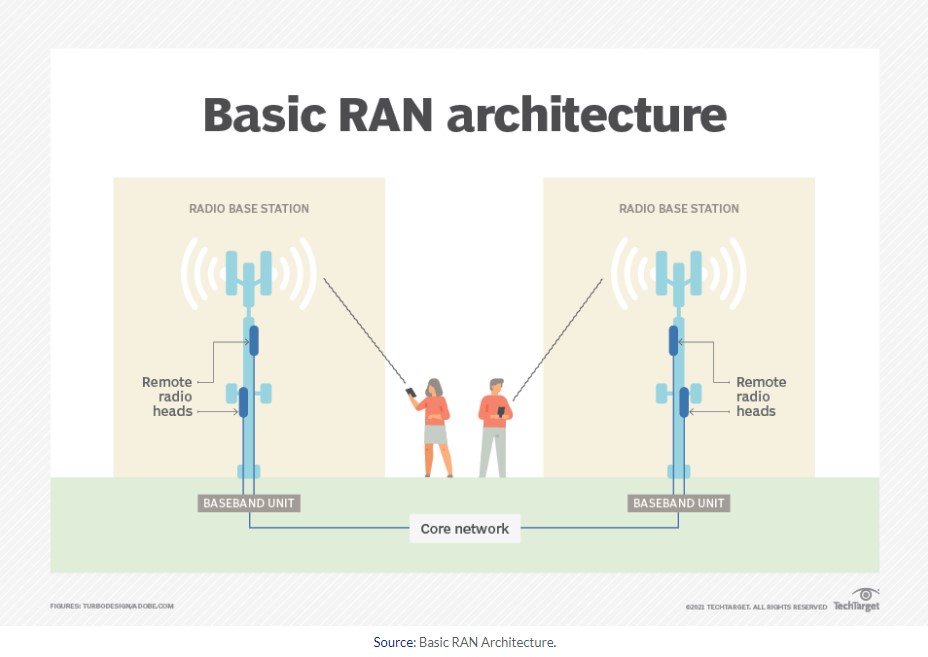
First, to be more understandable, it is good to describe the architecture of the primary radio internet. Radio networks have continuously improved from the first generation to the fifth. Current Ran technology can transmit voice calls and text messages and stream video and audio using the following essential elements to communicate data.
So the basic architecture of the radio network is a) the antenna for converting electrical signals into radio waves, b) the radios where they ensure the appropriate frequency bands and power levels to achieve communication, and c) the base units where the software is and the hardware that processes the signals and to be able to communicate wirelessly via radio waves.
Open Ran architecture or O-RAN
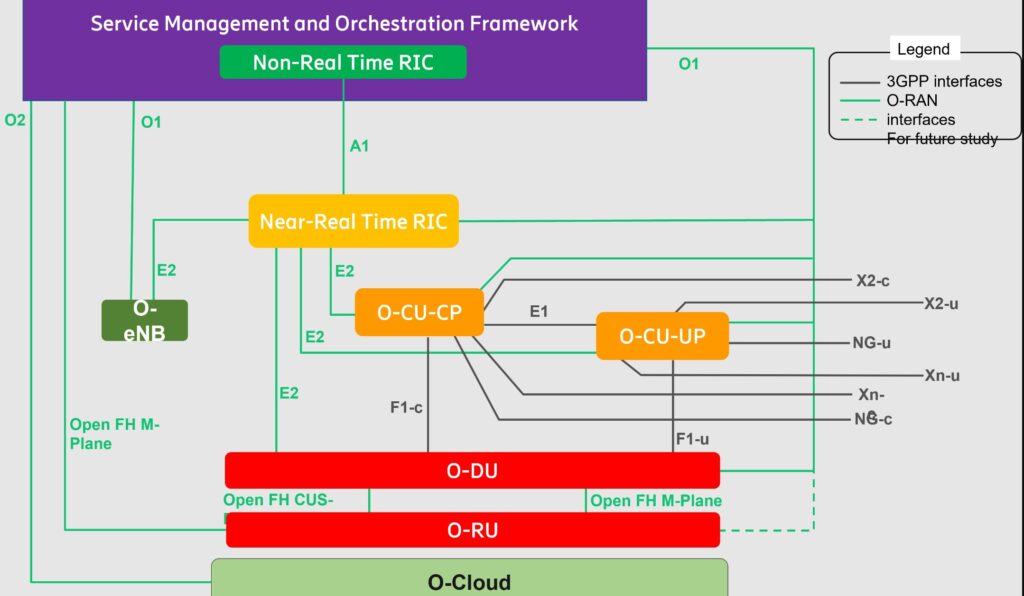
In the O-RAN architecture, the radio side includes Near-RT RIC, O-CU-CP, O-CU-UP, O-DU, and O-RU. The management side includes Service Management and Orchestration Framework that contains a Non-RT-RIC function.
Components Definition
near-RT RIC: O-RAN near-real-time RAN Intelligent Controller: a logical function that enables near-real-time control and optimization of O-RAN elements and resources via fine-grained data collection and actions over the E2 interface.
Non-RT RIC: O-RAN non-real-time RAN Intelligent Controller: a logical function that enables non-real-time control and optimization of RAN elements and resources, AI/ML workflow, including model training and updates, and policy-based guidance of applications/features in near-RT RIC.
NMS: A Network Management System
O-CU: O-RAN Central Unit: a logical node hosting RRC, SDAP and PDCP protocols
O-CU-CP: O-RAN Central Unit – Control Plane: a logical node hosting the RRC and the control plane part of the PDCP protocol
O-CU-UP: O-RAN Central Unit – User Plane: a logical node hosting the user plane part of the PDCP protocol and the SDAP protocol
O-DU: O-RAN Distributed Unit: a logical node hosting RLC/MAC/High-PHY layers based on a lower layer functional split.
O-RU: O-RAN Radio Unit: a logical node hosting the Low-PHY layer and RF processing based on a lower layer functional split. This is similar to 3GPP’s “TRP” or “RRH” but more specific in including the Low-PHY layer (FFT/iFFT, PRACH extraction).
O1: Interface between management entities in Service Management and Orchestration Framework and O-RAN managed elements for operation and management, by which FCAPS management, Software management, and File management shall be achieved.
O1*: Interface between Service Management and Orchestration Framework and Infrastructure Management Framework supporting O-RAN virtual network functions.
xAPP: Independent software plug-in to the Near-RT RIC platform to provide functional extensibility to the RAN by third parties.
Future Usage
Deutsche Telekom, Orange, Telecom Italia, Telefonica, and Vodafone have published a new report based on findings from independent firm Analysys Mason, calling on policymakers, EU member states, and industry stakeholders to prioritize an Open Radio Network (Open RAN), which will ensure, according to the companies themselves, that Europe continues to play a leading role in 5G and, in the future, 6G.
The report concludes that Europe needs to include Open RAN as a pillar in its Industrial Policy and Digital Compass strategy and support it with the proper policy framework. This will positively impact other important technology areas such as cloud, software, and circuits to significantly contribute to the broader technological ambitions of a digital Europe.

