Introduction
As is well known in the modern world, plastic is one of the main materials used to produce many goods and products that meet the requirements of consumers. Unfortunately, this created a problem in the natural environment due to overconsumption, the increase of human population but also at the same time the creation of products that are not a necessity because they are “unnecessary” in terms of basic human needs.
The very large development of the plastics industry with the significant problems posed by their disposal in the environment leads to the need for their recycling.
Plastic recycling technologies
The methods of collection are dictated either by law or by cultural peculiarities. However, in many countries there is no infrastructure for managing household waste in a useful way and they are sent to landfills.
An efficient technology of plastic recycling waste we should have:
- Development of waste separation and collective method
- Discovering more economical recycling methods
- Finding-developing markets capable, such that they can
- absorb the final products
- Quality control of recycled materials based on standards
The types of plastic waste that are recycled are divided into three categories:
- Types of plastics not mixed with other materials that can return to their original state through productive process from which they originated.
- Waste plastic mixtures that we know their composition, without plastic impurities.
- Household waste, whether industrial or commercial, which does not contain plastic impurities.
Depending on the type of plastic waste recycling process technology used, there are four categories:
1. Primary recycling
2. Secondary recycling
3. Tertiary recycling
4. Quaternary recycling
Primary recycling
This method is based on recovery defective products and by-products resulting from any industrial production process.
Three processes are now applied for their recycling:
Extrusion molding which homogenizes and plasticizes the feed. The method is based on a specially designed adiabatic extruder that feeds a system of linear molds, in conjunction with a cooling bath filled with water.
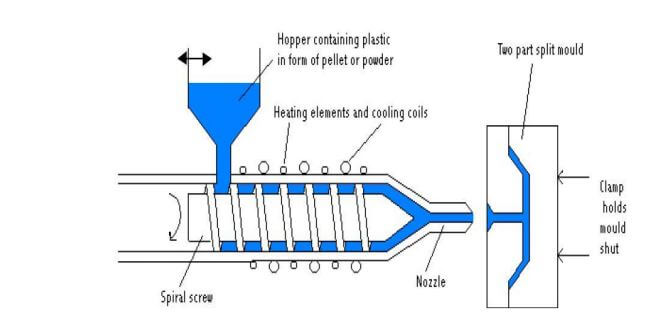
Injection molding. It is the most widely used technique of molding thermoplastics in discontinuous forms. According to it a thermoplastic polymer is introduced in the form flakes or powder where it is heated and melted. The liquid thermoplastic is then injected under high pressure through a suitable nozzle into the cold mold where it is cooled and solidified.
Blow molding. The blowing technique was initially used for the production of glass bottles and its use was extended to plastic bottles or generally hollow objects. In it, the polymer melt is passed through a cylindrical extrusion die to produce a cylindrical preform (parison)
Secondary Recycling
Refers to the treatment of waste containing various plastics in random compositions in order to produce a lower quality product.
Secondary recycling can only be applied to thermoplastic polymers and not to thermosets. Problems can arise from possible contamination of the material, which is why recycled plastics are not usually used in direct contact with food or beverages.
From a technological point of view there are two reservations: First, polymers are organic materials and their reheating for secondary recycling can lead to partial decomposition (degradation with reduction of the average molecular weight) and deterioration of their properties.
Second, different polymers cannot be easily mixed and their simple alloys have worse properties than their constituents. As there are many different types of polymers used (and discarded), waste must be able to be separated and identified by type of polymer, with precision, speed and low cost, so that secondary recycling is economically profitable as a process.

Tertiary Recycling
This is the treatment of the polymer with suitable chemicals reagents to break down the macromolecule into its monomers. These monomers are purified and repolymerized to form new non-degraded polymers, ready for molding into new products. Much research is taking place on the tertiary recycling of thermoset polymers and elastomers.
Tertiary recycling includes two categories’ processes based on the type of polymer being recycled:
- Chemical recycling and
- Thermal recycling.
Quaternary Recycling
Quaternary recycling is called the use of plastics waste as an energy source.
Modern waste plastic techniques
This is the controlled combustion of polymer waste in specially designed thermal power plants and its use their calorific value for electricity generation and district heating. Most polymers have a higher calorific value than carbon and argon. With this method, we also use plastic products as energy savers.
These state-of-the-art facilities minimize the problem of emissions of toxic substances into the environment. According to the quaternary recycling, household waste can be considered as a mixture of combustible, non-combustible materials and moisture.



