To begine with, let’s describe what is MFA (multifactor authentication) as this definition is mentioned in the interview.
Multi-Factor Authentication is a method of controlling access to a computer, which the user has access to only after successfully presenting several different elements in an authentication mechanism – usually at least two categories.
Its main purpose is to prevent unauthorized access to an account or device in the event of a password failure.
There are many ways you can add an MFA to an account. It may overlap with password-free connections, if the second and third steps in the login process including an email or SMS code or a scan of the user’s biometric data. The most common method involves the use of a one-time password (OTP) generated on a separate device. One of the aforementioned approaches is often lined with a connection badge that the user can scan or insert into the device in the form of a USB stick for connection.
Nichola in the login process with SMS code, can we have security or there is a danger of hacking and what is your suggestion for that?
“Well, unfortunately there is a way with social engineering to infringement from a hacker. Hypr company offers the way to solve this scenario. Let me describe the Hypr cloud platform, so to be clear with technical details.”
The following description is from Nicholas Zikos. He is starting with the HYPR cloud platform and continues with more specific things relevant to the MFA method access through Windows and Mac.
The HYPR Cloud Platform
The HYPR Cloud Platform is designed to eliminate passwords and shared secrets across the enterprise. By removing the hackers’ primary target, HYPR forces the adversary to attack each device individually – drastically shifting the economics of an attack back in your favour.
HYPR supports a variety of use cases, applications and environments. Here you’ll find everything you need to deploy passwordless authentication to your workforce and your customers.
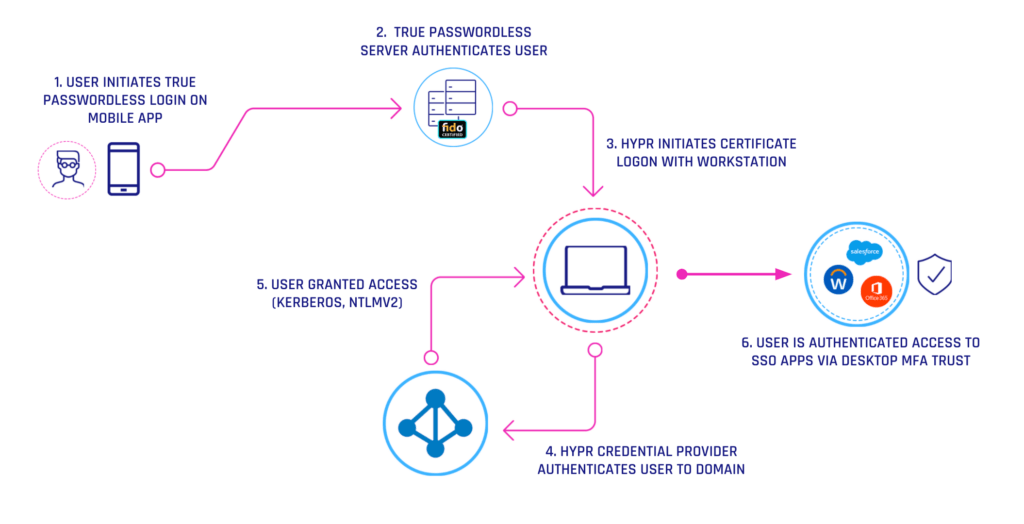
HYPR Workforce Access for Windows
HYPR turns your smartphone into a smart card. By combining public-key encryption with lightning-fast mobile-initiated authentication, HYPR enables passwordless login to workstations through your mobile device.
The HYPR Workforce Access Client is designed to ensure each workforce user has a convenient, productive, and secure experience when accessing their Windows workstations. Once deployed, users can unlock their Windows workstations without a password by using their mobile devices.
How it works
HYPR is utilizing certificate-based authentication to login into Windows user accounts. When the user pairs the mobile device with the computer, virtual smartcard will be created to perform the authentication.
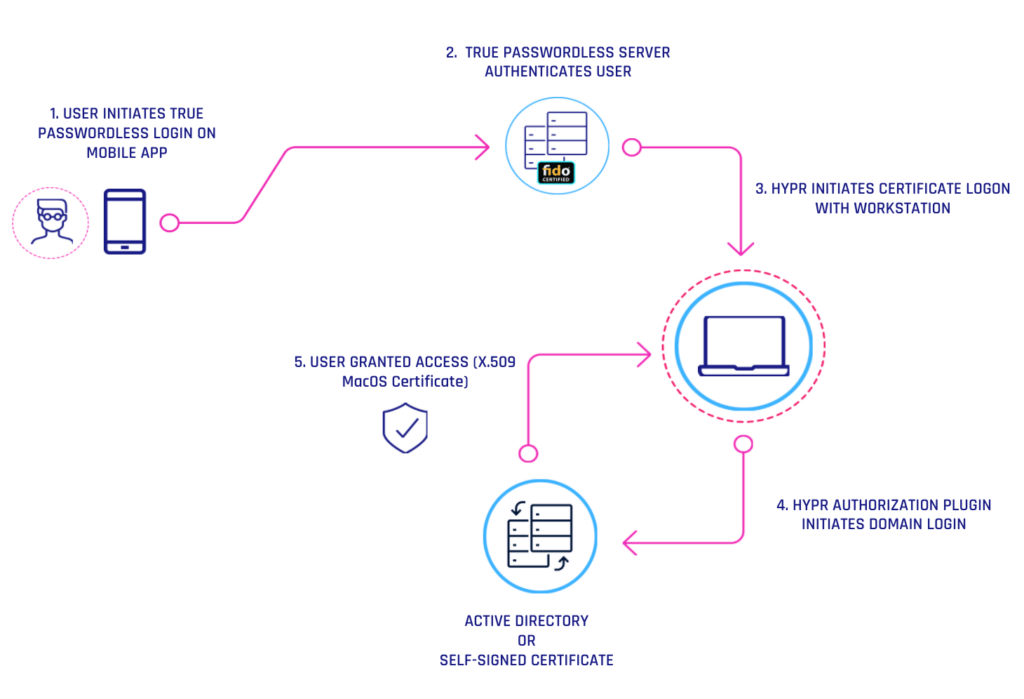
HYPR Workforce Access for Mac
By combining public-key encryption with lightning-fast mobile-initiated authentication, HYPR enables passwordless login to workstations through your mobile device.
The HYPR Workforce Access client for macOS was designed to ensure each employee has a convenient, more productive, and secure experience accessing macOS workstations. Once deployed, employees can unlock their macOS workstations utilizing authentication with their mobile devices.
Extensions
Extensions are integrations in the HYPR Control Center which facilitate the operation of external systems at predetermined points in the Registration and Authentication lifecycle.
Example: Once the user is successfully registered, we might want to update the user’s record in an external system. In this situation we can write an extension which receives a registration call-back and calls out to the external system.
An extension is not an external process. It is a Java jar which runs in process with the Control Center and is managed via the Control Center UI. This eliminates the need to manage separate processes.

Courtesy of HYPR – Structure of an Extension 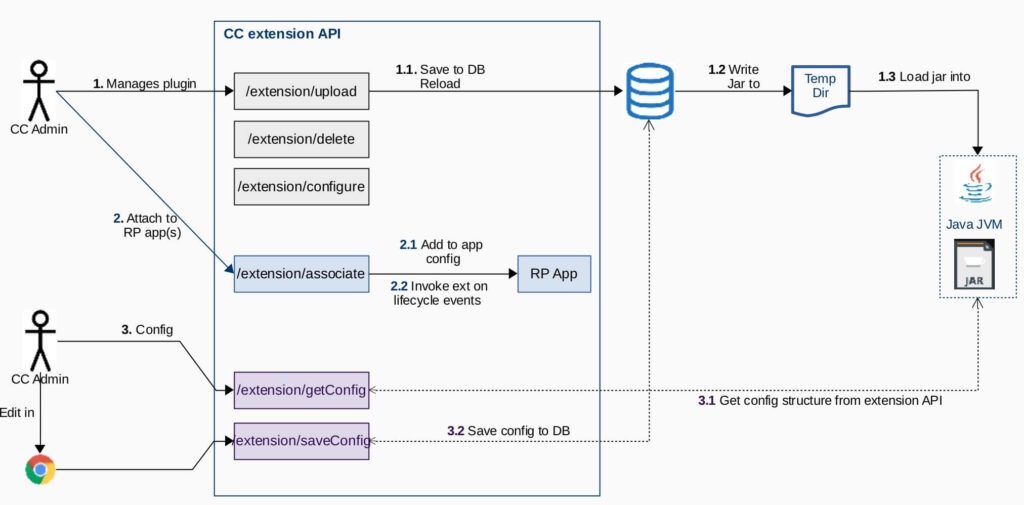
Courtesy of HYPR – Structure of an Extension
Each extension is uniquely identified by a ExtensionId. Extensions are managed at a global level which are available to all Relying Party Applications. Once an extension is deployed, it may be associated with one or more RP Applications via the Control Center web UI.
An extension is a container for one or more Extension Points. An Extension Point is
- where we specify the logic, we want to execute
- contains a series of call-backs which are invoked by the Control Center
- contains configuration call-back which is invoked by the Control Center
Upon execution, an extension method can
- Execute desired logic or calls to external systems
- Return a response indicating success or failure
- Throw an exception, which is considered an execution failure



