Proximity medicine: The metaverse is a technological dimension that, contrary to popular belief, will transcend the world of games and entertainment, generating profound transformations in the healthcare sector as well. In fact, 77 per cent of providers and 94 per cent of global customers in the sector expect increasing involvement in the coming years. Indeed, this technology has enabled several companies to achieve results with greater accessibility and reduced costs, particularly in the fields of medical and surgical imaging, mental health, and medical education. Undoubtedly an opportunity for companies which must now understand how to approach this phenomenon.
This is stated in the latest Bcg study, ‘The Health Care Metaverse Is More Than a Virtual Reality’, based on a global survey of suppliers, customers and biopharma and medtech companies, which showed that most companies are already conducting experiments with these technologies. Current applications in the field of digital healthcare mainly concern so-called ‘extended realities’ (XR), i.e. the combination of visual and immersive experiences offered by augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR) and mixed reality (MR).
Still, they can also use Web3 technologies and applications, such as blockchain and virtual resources, and M-worlds, i.e. virtual ‘places’ where people can meet and create content. Technologies that can produce value for businesses in a variety of ways, such as improving access to care by connecting patients and providers without the constraint of geographic location, improving the accuracy of diagnosis and quality of surgery, reducing costs for supplies, medical training, and data management, and much more. Bcg research shows that three-quarters of healthcare providers and more than a third of customers surveyed said they use XR, blockchain and M-worlds.
Possible developments
Although XR technology is the least used by customers, 25% use blockchain. In addition, 90% of executive respondents say they believe the importance of the metaverse will increase, as will engagement for companies. However, only 17% of suppliers and 6% of customers have started or are developing pilot programs. Most have yet to define a vision and adopt a dedicated strategy for implementing these technologies.
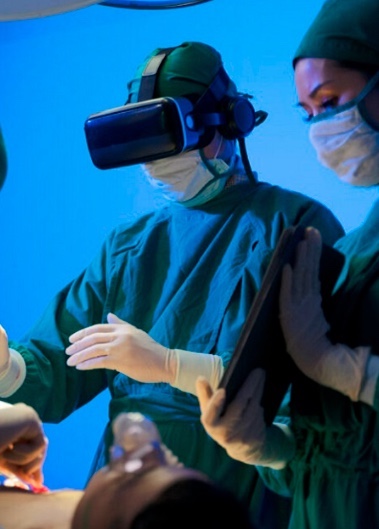
Some examples of products already available on the market are those made by companies working with ARs to assist medical procedures, including surgical preparation and the performance of spine operations. Then some technologies enable full visualization of the patient’s anatomy, improving error rates, speed, and results. Other applications may relate to rehabilitation, physical therapies, and treatments for anxiety, phobias, and post-traumatic stress.
The phases of adoption and development of the metaverse
The development of the metaverse in the medical area will take place in three phases: the initial period of experimentation, in which we are now; the gradual adoption of existing use cases and the emergence of new ones fueled by ongoing technological progress, which will take place over the next five years; and the third phase, with new use cases on the one hand and the standardization of metaverse technologies in various areas of healthcare on the other. Two-thirds of the providers and half of the customers surveyed believe that investments are needed either in the phase we are in now – of experimentation – or soon (two to three years from now).
Indeed, the development speed of the metaverse will depend on the wider adoption of the underlying technologies in three key business areas: technology tools (such as the deployment of virtual reality displays), content and usage models. Other factors to consider will be the interaction of B2B and B2C companies with users in metaverse environments, as well as the integration of new technologies with current systems and the development of new solutions to accelerate the adoption of these technologies. Finally, it will be necessary to design an effective metaverse interaction experience to ensure understanding for a wide audience; then create a digital twin strategy, integrating metaverse use cases into operations from the outset; develop the necessary skills, and create control teams with clear mandates and processes to monitor and oversee the various stages of business development in the virtual world.



